How Mutual Banks can 'Hollow out their Core' by moving from Monolithic to Microservices
In recent years, Australian mutual banks and financial providers have been undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the need to stay competitive in an increasingly digital and fast-paced financial environment.
A notable trend emerging from this shift is the hollowing out of traditional core banking systems.
A notable trend emerging from this shift is the hollowing out of traditional core banking systems. The reasons behind this phenomenon, its implications, and how mutual banks are navigating these changes rely on the concept of ‘reinvention’ as much as the actions of transformation.
Understanding the Hollowing Out Trend
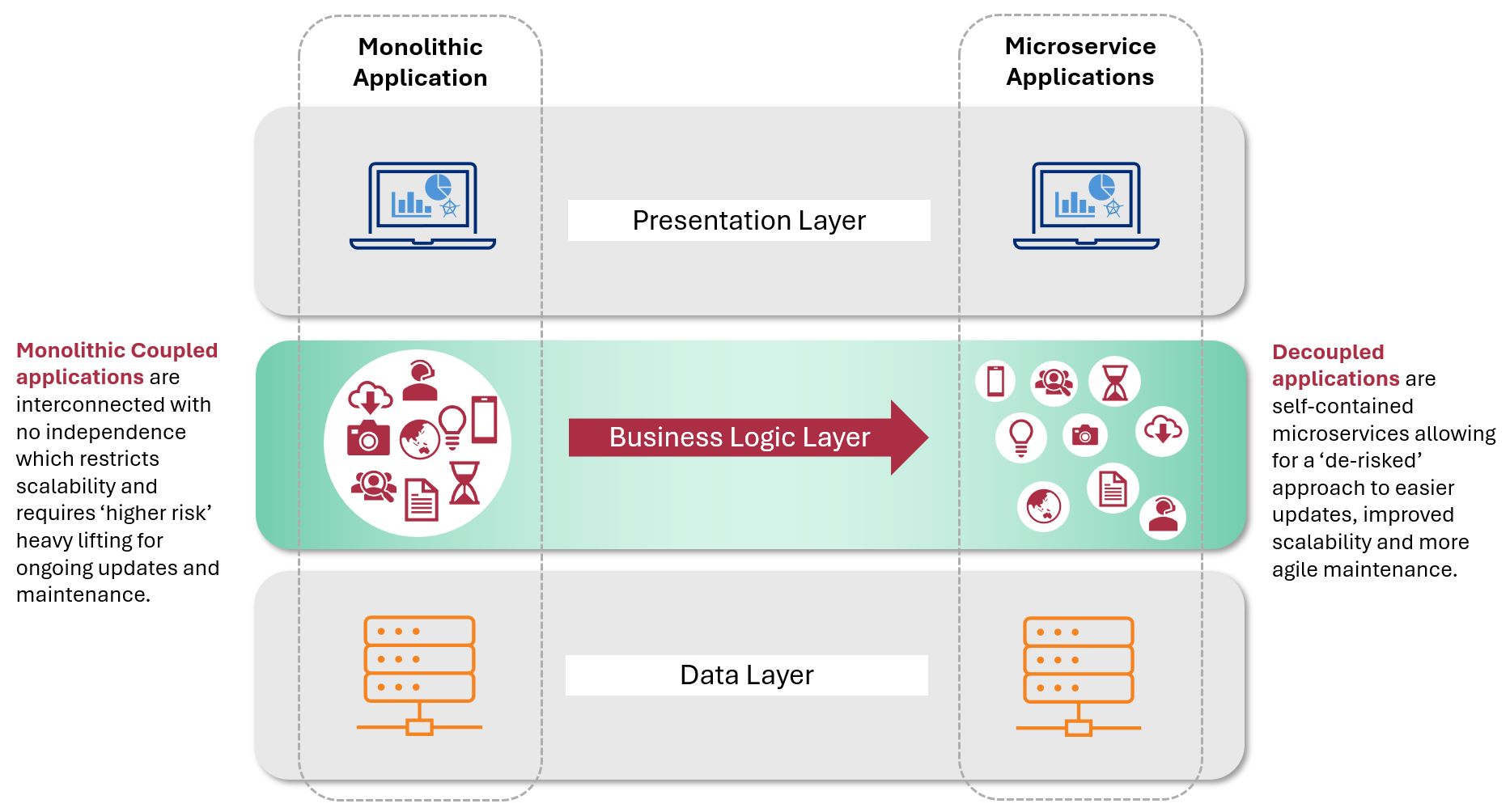
The hollowing out of core banking systems refers to the process where mutual banks are moving away from traditional, monolithic core banking platforms towards more modular and flexible solutions.
This shift involves either replacing or supplementing existing systems with specialised technologies that can handle specific functions such as digital banking, customer relationship management (CRM), or risk management.
Drivers of Change
Customer Expectations: With the rise of digital banking, customers now expect seamless, real-time interactions and a high level of personalisation. Traditional core systems, often built decades ago, struggle to meet these modern demands efficiently.
Technological Advancements: New technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning offer enhanced capabilities that traditional core systems cannot match. These technologies enable better data analytics, improved security, and more agile operations.
Regulatory Requirements: Increasingly stringent regulatory standards require more sophisticated risk management and compliance tools. Traditional core banking systems often fall short in adapting to these evolving requirements.
Cost Efficiency: Maintaining and upgrading legacy systems can be costly. By transitioning to more modular solutions, mutual banks can reduce their reliance on expensive legacy infrastructure and invest in innovative technologies that offer better value.
Implications for Mutual Banks
Enhanced Flexibility and Innovation: By moving away from monolithic core systems, mutual banks can adopt a best-of-breed approach, integrating various specialised solutions that better meet their needs. This flexibility allows for quicker adoption of new technologies and more innovative services.
Improved Customer Experience: Modular systems enable better integration with digital channels, providing a more seamless and personalised customer experience. Banks can offer features such as real-time transaction notifications, personalised product selection, and more user-friendly interfaces.
Operational Efficiency: Modern systems can automate many manual processes, reducing errors and operational costs. This efficiency is crucial for mutual banks aiming to remain competitive against larger financial institutions.
Data-Driven Insights: Advanced analytics and AI capabilities allow mutual banks to gain deeper insights into customer behaviour and preferences, leading to more targeted marketing and improved risk management.
While the transition presents challenges, careful planning and strategic implementation can lead to substantial benefits and a stronger position in the market.
Navigating the Transition
Strategic Planning: Mutual banks need a clear strategy for transitioning from legacy systems to modern solutions. This includes assessing their current systems, identifying gaps, and selecting appropriate technologies that align with their strategic goals.
Vendor Selection: Choosing the right technology partners is critical. Mutual banks should look for vendors with a proven track record, scalable solutions, and the ability to integrate seamlessly with existing systems.
Change Management: Transitioning to new systems requires careful change management. Ensuring that staff are trained and that there is minimal disruption to operations is essential for a smooth transition.
Regulatory Compliance: As they adopt new technologies, mutual banks must ensure that their systems comply with all regulatory requirements. Working with vendors who understand the regulatory landscape can help mitigate compliance risks.
The hollowing out of core banking systems in Australian mutual banks represents a significant shift towards more agile, customer-centric, and technologically advanced operations.
The hollowing out of core banking systems in Australian mutual banks represents a significant shift towards more agile, customer-centric, and technologically advanced operations. By moving away from traditional monolithic systems and embracing modular solutions, mutual banks can enhance their flexibility, improve customer experiences, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving financial environment.
While the transition presents challenges, careful planning and strategic implementation can lead to substantial benefits and a stronger position in the market.
If you will play a part in helping to deliver your Bank's transformation goals, and are interested in exploring how you can move from traditional core banking systems to more modular solutions to improve customer experiences, reduce costs and give you a competitive edge, then Let’s talk.
